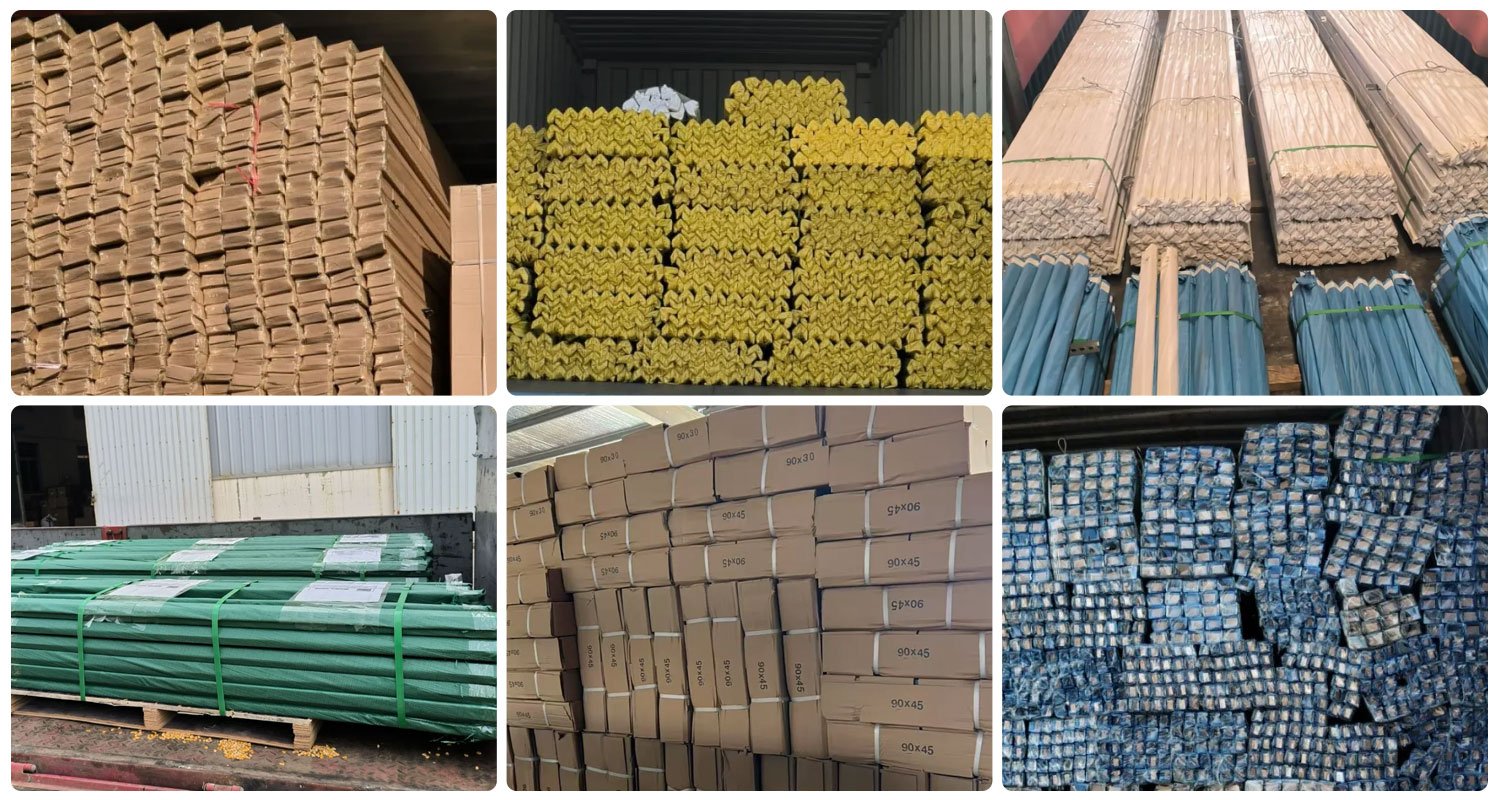
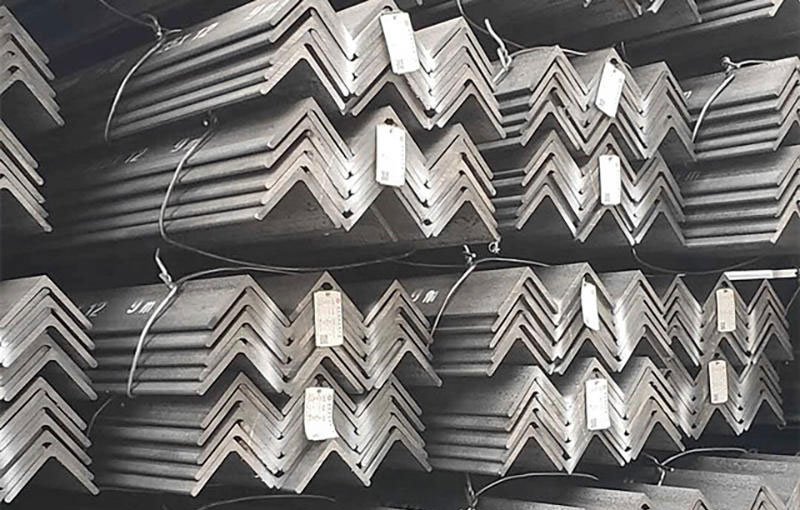
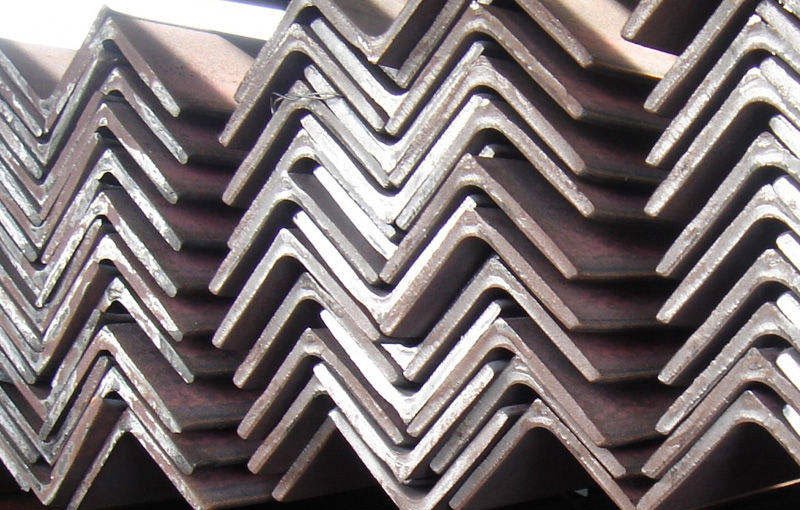
Carbon steel angle
Product Introduction
| Parameter Category | Parameter Name | Unit | Description & Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Identification | Material Grade | — | Carbon steel grade (e.g., ASTM A36, EN 10025-2 S235JR, GB/T 700 Q235B, JIS G3101 SS400) |
| Standard Compliance | — | Governing standard (e.g., ASTM A6/A6M, EN 10210-1, GB/T 706, JIS Z3352) | |
| Channel Type | — | Classification by manufacturing process: – Hot-Rolled Carbon Steel Channel (most common) – Cold-Formed Carbon Steel Channel (for light-duty applications) | |
| Dimensional Parameters | Depth of Channel (h) | mm/inch | Distance from the top of one flange to the top of the opposite flange (cross-sectional height). Typical range: 50–400 mm (2–16 inches) (e.g., C5: 50 mm; C16: 160 mm per ASTM). |
| Width of Flange (b) | mm/inch | Width of the horizontal “flange” (the two parallel sides of the “U”). Typical range: 25–150 mm (1–6 inches) | |
| Thickness of Web (d) | mm/inch | Thickness of the vertical “web” (the middle part of the “U” connecting the two flanges). Typical range: 3–12 mm (0.12–0.47 inches) | |
| Thickness of Flange (t) | mm/inch | Thickness of the flange (often slightly thicker than the web for structural stability). Typical range: 4–15 mm (0.16–0.59 inches) | |
| Root Radius (r) | mm/inch | Radius of the curve where the web meets the flange (reduces stress concentration). Typical range: 5–15 mm (0.2–0.6 inches) | |
| Toe Radius (r₁) | mm/inch | Radius of the outer edge of the flange (improves safety and structural integrity). Typical range: 2–8 mm (0.08–0.31 inches) | |
| Length (L) | m/ft | Standard length: 6–12 m (20–40 ft); custom lengths available (shortened or extended) | |
| Mechanical Properties | Yield Strength (ReH) | MPa/ksi | Minimum yield strength (varies by grade): – ASTM A36: ≥250 MPa (36 ksi) – S235JR: ≥235 MPa (34 ksi) – Q235B: ≥235 MPa (34 ksi) |
| Tensile Strength (Rm) | MPa/ksi | Ultimate tensile strength: – ASTM A36: 400–550 MPa (58–80 ksi) – S235JR: 360–510 MPa (52–74 ksi) – Q235B: 375–500 MPa (54–73 ksi) | |
| Elongation at Break (A) | % | Minimum elongation (over 50 mm gauge length): – ASTM A36: ≥20% – S235JR: ≥26% – Q235B: ≥26% | |
| Impact Toughness (Charpy V-Notch) | J | Energy absorbed at specified temperature (varies by grade): – Q235B: ≥27 J at 20°C – Q235D: ≥27 J at -40°C – S235JR: ≥27 J at 20°C | |
| Chemical Composition (Typ.) | Carbon (C) | % | 0.17–0.24% (varies by grade; e.g., Q235B: ≤0.22%) |
| Manganese (Mn) | % | 0.30–1.60% (e.g., ASTM A36: 0.80–1.20%) | |
| Phosphorus (P) | % | Maximum: 0.045% (to prevent brittleness) | |
| Sulfur (S) | % | Maximum: 0.045% (to reduce hot cracking) | |
| Silicon (Si) | % | 0.12–0.30% (optional, for deoxidation) | |
| Surface & Finish | Surface Treatment | — | – Mill Finish: As-rolled (with oxide scale, suitable for indoor use) – Hot-Dip Galvanized (HDG): Zn-coating (≥65 μm thickness, for corrosion resistance in outdoor/harsh environments) – Painted: Epoxy or polyester coating |
| Surface Quality | — | Free from cracks, folds, delaminations, or excessive scale (per standard requirements; e.g., EN 10025-1 Class A/B) | |
| Weight & Density | Theoretical Weight per Unit Length | kg/m/lb/ft | Calculated based on cross-sectional area (e.g., C10×15.3 ASTM: 15.3 lb/ft ≈22.7 kg/m; Q235B 10# channel: 10.007 kg/m per GB/T 706) |
| Density of Carbon Steel | g/cm³ | 7.85 g/cm³ (standard for carbon steel) |
| Standard & Grade | C (Carbon) (Max. / Typ. %) | Mn (Manganese) (Max. / Typ. %) | Si (Silicon) (Max. / Typ. %) | P (Phosphorus) (Max. %) | S (Sulfur) (Max. %) | Cu (Copper) (Max. / Typ. %) | Other Elements (Max. %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A36 (USA) | 0.25 / 0.20 | 1.20 / 1.00 | 0.40 / 0.25 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.20 / — | — (No mandatory limits for Ni, Cr, Mo unless specified) |
| EN 10025-2 S235JR (EU) | 0.17 / 0.15 | 1.60 / 1.00 | 0.55 / 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.55 / — | Ni: 0.30; Cr: 0.30; Mo: 0.10; Nb: 0.015 |
| GB/T 700 Q235A (China) | 0.22 / 0.20 | 1.40 / 0.80 | 0.35 / 0.20 | 0.045 | 0.050 | — / — | — |
| GB/T 700 Q235B (China) | 0.22 / 0.20 | 1.40 / 0.80 | 0.35 / 0.20 | 0.045 | 0.045 | — / — | — |
| GB/T 700 Q235D (China) | 0.17 / 0.15 | 1.40 / 0.80 | 0.35 / 0.20 | 0.035 | 0.035 | — / — | — |
| JIS G3101 SS400 (Japan) | 0.23 / 0.20 | 1.60 / 1.00 | 0.35 / 0.25 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.30 / — | Ni: 0.30; Cr: 0.30; Mo: 0.10 |
| Standard & Grade | Yield Strength σs (MPa) | Tensile Strength σb (MPa) | Elongation δ5 (%) | Reduction of Area ψ (%) | Impact Energy Akv (J) | Hardness | Density | Shear Strength | Melting Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A36[2,6] | 315 | 400 | 23 | — | — | 140HB | 7.8 g/cm³ | 300 MPa | 1420 – 1460 °C |
| EN 10025-2 S235JR | ≥235 | ≥360 – 510 | ≥26 | — | ≥27 at 20°C | — | — | — | — |
| GB/T 700 Q235A[4] | ≤16mm: ≥215 16 – 40mm: ≥205 40 – 60mm: ≥195 60 – 100mm: ≥185 100 – 150mm: ≥175 >150mm: ≥165 | 335 – 450 | ≤16mm: ≥31 16 – 40mm: ≥30 40 – 60mm: ≥29 60 – 100mm: ≥28 100 – 150mm: ≥27 >150mm: ≥26 | — | ≥27 at 20°C | — | — | — | — |
| GB/T 700 Q235B | Similar to Q235A | Similar to Q235A | Similar to Q235A | — | ≥27 at 20°C | — | — | — | — |
| GB/T 700 Q235D | ≥235 | ≥370 – 500 | ≥22 | — | ≥27 at -20°C | — | — | — | — |
| EN 10025-2 S275JR | ≥275 | ≥410 – 560 | ≥23 | — | ≥27 at 20°C | — | — | — | — |
| EN 10025-2 S355JR | ≥355 | ≥470 – 630 | ≥20 | — | ≥27 at 20°C | — | — | — | — |

Packaging and transportation
8unit in 1*20GP container , 12units in 1*40HQ container, Fumigated wood tray and 10mm wire fixed.